1632. Rank Transform of a Matrix
Description
Given an m x n matrix, return a new matrix answer where answer[row][col] is the rank of matrix[row][col].
The rank is an integer that represents how large an element is compared to other elements. It is calculated using the following rules:
- The rank is an integer starting from
1. - If two elements
pandqare in the same row or column, then:- If
p < qthenrank(p) < rank(q) - If
p == qthenrank(p) == rank(q) - If
p > qthenrank(p) > rank(q)
- If
- The rank should be as small as possible.
The test cases are generated so that answer is unique under the given rules.
Example 1:
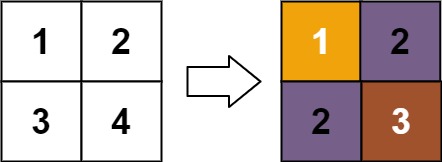
Input: matrix = [[1,2],[3,4]] Output: [[1,2],[2,3]] Explanation: The rank of matrix[0][0] is 1 because it is the smallest integer in its row and column. The rank of matrix[0][1] is 2 because matrix[0][1] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1. The rank of matrix[1][0] is 2 because matrix[1][0] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1. The rank of matrix[1][1] is 3 because matrix[1][1] > matrix[0][1], matrix[1][1] > matrix[1][0], and both matrix[0][1] and matrix[1][0] are rank 2.
Example 2:
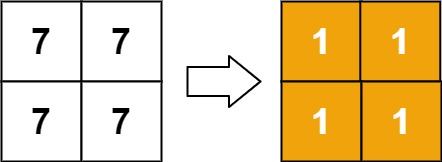
Input: matrix = [[7,7],[7,7]] Output: [[1,1],[1,1]]
Example 3:
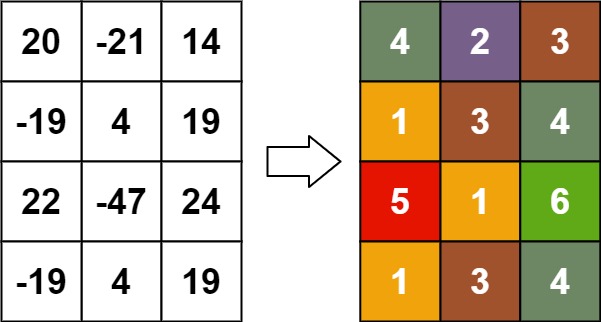
Input: matrix = [[20,-21,14],[-19,4,19],[22,-47,24],[-19,4,19]] Output: [[4,2,3],[1,3,4],[5,1,6],[1,3,4]]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500-109 <= matrix[row][col] <= 109
Solutions
Solution: Union Find
- Time complexity: O(mnlogmn)
- Space complexity: O(mn)
JavaScript
js
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @return {number[][]}
*/
const matrixRankTransform = function (matrix) {
const m = matrix.length;
const n = matrix[0].length;
const valueMap = new Map();
for (let row = 0; row < m; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
const value = matrix[row][col];
if (!valueMap.has(value)) {
valueMap.set(value, []);
}
valueMap.get(value).push({ row, col });
}
}
const sortedValues = [...valueMap.keys()].toSorted((a, b) => a - b);
const ranks = Array.from({ length: m + n }, () => 0);
const result = Array.from({ length: m }, () => new Array(n).fill(0));
for (const value of sortedValues) {
const uf = new UnionFind();
for (const { row, col } of valueMap.get(value)) {
uf.union(row, col + m);
}
const groups = uf.getGroups();
for (const ids of groups.values()) {
let maxRank = 0;
for (const id of ids) {
maxRank = Math.max(ranks[id], maxRank);
}
for (const id of ids) {
ranks[id] = maxRank + 1;
}
}
for (const { row, col } of valueMap.get(value)) {
result[row][col] = ranks[row];
}
}
return result;
};
class UnionFind {
constructor() {
this.groupMap = new Map();
}
find(x) {
if (!this.groupMap.has(x)) {
this.groupMap.set(x, x);
}
if (this.groupMap.get(x) !== x) {
const group = this.groupMap.get(x);
this.groupMap.set(x, this.find(group));
}
return this.groupMap.get(x);
}
union(x, y) {
const groupX = this.find(x);
const groupY = this.find(y);
if (groupX === groupY) return false;
this.groupMap.set(groupX, groupY);
return true;
}
getGroups() {
const groups = new Map();
for (const x of this.groupMap.keys()) {
const group = this.find(x);
if (!groups.has(group)) {
groups.set(group, []);
}
groups.get(group).push(x);
}
return groups;
}
}