1382. Balance a Binary Search Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary search tree, return a balanced binary search tree with the same node values. If there is more than one answer, return any of them.
A binary search tree is balanced if the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than 1.
Example 1:
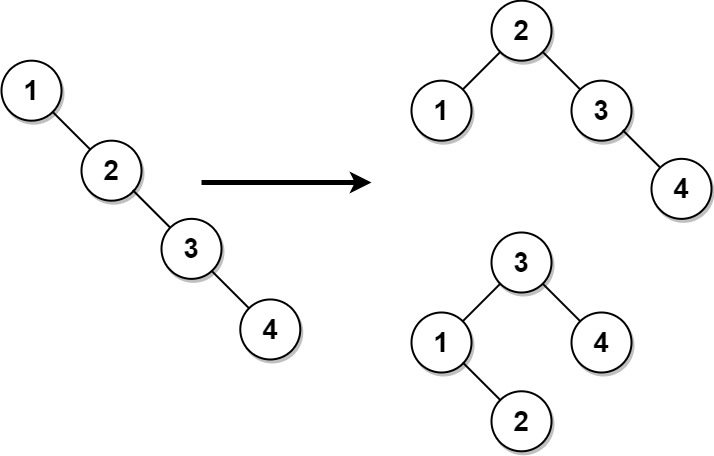
Input: root = [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,null] Output: [2,1,3,null,null,null,4] Explanation: This is not the only correct answer, [3,1,4,null,2] is also correct.
Example 2:
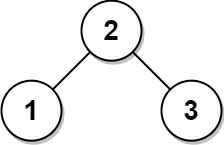
Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: [2,1,3]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105
Solutions
Solution: Depth-First Search
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
JavaScript
js
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
const balanceBST = function (root) {
const values = [];
const getBSTValue = node => {
if (!node) return;
const { val, left, right } = node;
values.push(val);
getBSTValue(left);
getBSTValue(right);
};
getBSTValue(root);
values.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const createBST = (start, end) => {
if (start > end) return null;
const mid = Math.floor((start + end) / 2);
const node = new TreeNode(values[mid]);
node.left = createBST(start, mid - 1);
node.right = createBST(mid + 1, end);
return node;
};
return createBST(0, values.length - 1);
};