2684. Maximum Number of Moves in a Grid
Description
You are given a 0-indexed m x n matrix grid consisting of positive integers.
You can start at any cell in the first column of the matrix, and traverse the grid in the following way:
- From a cell
(row, col), you can move to any of the cells:(row - 1, col + 1),(row, col + 1)and(row + 1, col + 1)such that the value of the cell you move to, should be strictly bigger than the value of the current cell.
Return the maximum number of moves that you can perform.
Example 1:
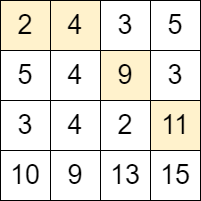
Input: grid = [[2,4,3,5],[5,4,9,3],[3,4,2,11],[10,9,13,15]] Output: 3 Explanation: We can start at the cell (0, 0) and make the following moves: - (0, 0) -> (0, 1). - (0, 1) -> (1, 2). - (1, 2) -> (2, 3). It can be shown that it is the maximum number of moves that can be made.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[3,2,4],[2,1,9],[1,1,7]] Output: 0 Explanation: Starting from any cell in the first column we cannot perform any moves.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 10004 <= m * n <= 1051 <= grid[i][j] <= 106
Solutions
Solution: Dynamic Programming
- Time complexity: O(mn)
- Space complexity: O(m)
JavaScript
js
/**
* @param {number[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
const maxMoves = function (grid) {
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
let dp = new Array(m + 1).fill(0);
for (let col = n - 2; col >= 0; col--) {
const nextDp = new Array(m + 1).fill(0);
for (let row = 0; row < m; row++) {
const value = grid[row][col];
const upper = grid[row - 1]?.[col + 1];
const middle = grid[row][col + 1];
const lower = grid[row + 1]?.[col + 1];
const index = row + 1;
const upperStep = value < upper ? dp[index - 1] + 1 : 0;
const middleStep = value < middle ? dp[index] + 1 : 0;
const lowerStep = value < lower ? dp[index + 1] + 1 : 0;
nextDp[index] = Math.max(upperStep, middleStep, lowerStep);
}
dp = nextDp;
}
return Math.max(...dp);
};