861. Score After Flipping Matrix
Description
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid.
A move consists of choosing any row or column and toggling each value in that row or column (i.e., changing all 0's to 1's, and all 1's to 0's).
Every row of the matrix is interpreted as a binary number, and the score of the matrix is the sum of these numbers.
Return the highest possible score after making any number of moves (including zero moves).
Example 1:
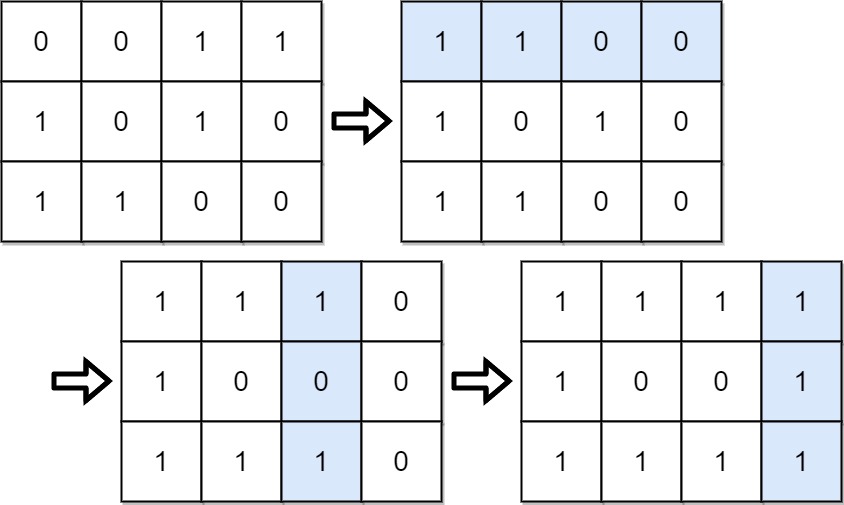
Input: grid = [[0,0,1,1],[1,0,1,0],[1,1,0,0]] Output: 39 Explanation: 0b1111 + 0b1001 + 0b1111 = 15 + 9 + 15 = 39
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[0]] Output: 1
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 20grid[i][j]is either0or1.
Solutions
Solution: Greedy
- Time complexity: O(mn)
- Space complexity: O(mn)
JavaScript
js
/**
* @param {number[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
const matrixScore = function (grid) {
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
for (let row = 0; row < m; row++) {
if (grid[row][0] === 1) continue;
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
grid[row][col] = grid[row][col] ? 0 : 1;
}
}
for (let col = 1; col < n; col++) {
let count = 0;
for (let row = 0; row < m; row++) {
if (grid[row][col]) count += 1;
}
if (count >= m / 2) continue;
for (let row = 0; row < m; row++) {
grid[row][col] = grid[row][col] ? 0 : 1;
}
}
return grid.reduce((result, row) => {
return result + Number.parseInt(row.join(''), 2);
}, 0);
};