1289. Minimum Falling Path Sum II
Description
Given an n x n integer matrix grid, return the minimum sum of a falling path with non-zero shifts.
A falling path with non-zero shifts is a choice of exactly one element from each row of grid such that no two elements chosen in adjacent rows are in the same column.
Example 1:
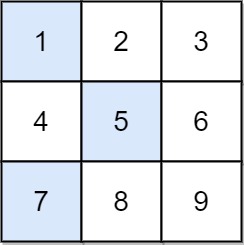
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: 13 Explanation: The possible falling paths are: [1,5,9], [1,5,7], [1,6,7], [1,6,8], [2,4,8], [2,4,9], [2,6,7], [2,6,8], [3,4,8], [3,4,9], [3,5,7], [3,5,9] The falling path with the smallest sum is [1,5,7], so the answer is 13.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[7]] Output: 7
Constraints:
n == grid.length == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 200-99 <= grid[i][j] <= 99
Solutions
Solution: Dynamic Programming
- Time complexity: O(n2)
- Space complexity: O(n)
JavaScript
js
/**
* @param {number[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
const minFallingPathSum = function (grid) {
const n = grid.length;
const dp = [...grid[0]];
for (let row = 1; row < n; row++) {
let first = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
let second = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
let index = -1;
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (dp[col] < first) {
second = first;
first = dp[col];
index = col;
} else if (dp[col] < second) second = dp[col];
}
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
const value = grid[row][col];
dp[col] = index === col ? value + second : value + first;
}
}
return Math.min(...dp);
};