1895. Largest Magic Square
Description
A k x k magic square is a k x k grid filled with integers such that every row sum, every column sum, and both diagonal sums are all equal. The integers in the magic square do not have to be distinct. Every 1 x 1 grid is trivially a magic square.
Given an m x n integer grid, return the size (i.e., the side length k) of the largest magic square that can be found within this grid.
Example 1:
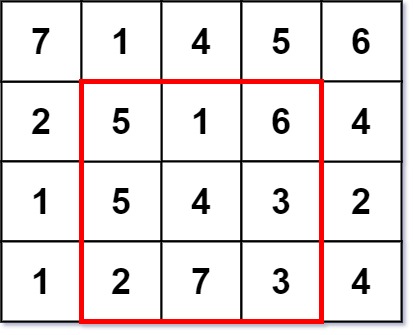
Input: grid = [[7,1,4,5,6],[2,5,1,6,4],[1,5,4,3,2],[1,2,7,3,4]] Output: 3 Explanation: The largest magic square has a size of 3. Every row sum, column sum, and diagonal sum of this magic square is equal to 12. - Row sums: 5+1+6 = 5+4+3 = 2+7+3 = 12 - Column sums: 5+5+2 = 1+4+7 = 6+3+3 = 12 - Diagonal sums: 5+4+3 = 6+4+2 = 12
Example 2:
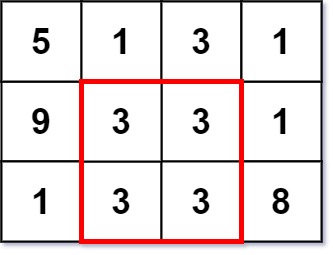
Input: grid = [[5,1,3,1],[9,3,3,1],[1,3,3,8]] Output: 2
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 501 <= grid[i][j] <= 106
Solutions
Solution: Prefix Sum
- Time complexity: O(mn*min(m,n)2)
- Space complexity: O(mn)
JavaScript
js
/**
* @param {number[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
const largestMagicSquare = function (grid) {
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
const rowSums = new Array(m).fill('').map(_ => new Array(n + 1).fill(0));
const colSums = new Array(n).fill('').map(_ => new Array(m + 1).fill(0));
const boundary = Math.min(m, n);
const isValid = (sum, row, col, boundary) => {
for (let length = 0; length < boundary; length++) {
const rowSum = rowSums[row + length][col + boundary] - rowSums[row + length][col];
const colSum = colSums[col + length][row + boundary] - colSums[col + length][row];
if (sum !== rowSum || sum !== colSum) return false;
}
return true;
};
const isValidDiagonal = (sum, row, col, boundary) => {
let diagonal1 = 0;
let diagonal2 = 0;
for (let length = 0; length < boundary; length++) {
diagonal1 += grid[row + length][col + length];
diagonal2 += grid[row + length][col + boundary - length - 1];
}
return sum === diagonal1 && sum === diagonal2;
};
for (let row = 0; row < m; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
const value = grid[row][col];
rowSums[row][col + 1] = rowSums[row][col] + value;
colSums[col][row + 1] = colSums[col][row] + value;
}
}
for (let length = boundary; length > 1; length--) {
for (let row = 0; row <= m - length; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col <= n - length; col++) {
const sum = rowSums[row][col + length] - rowSums[row][col];
if (!isValid(sum, row, col, length)) continue;
if (isValidDiagonal(sum, row, col, length)) return length;
}
}
}
return 1;
};