1761. Minimum Degree of a Connected Trio in a Graph
Description
You are given an undirected graph. You are given an integer n which is the number of nodes in the graph and an array edges, where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between ui and vi.
A connected trio is a set of three nodes where there is an edge between every pair of them.
The degree of a connected trio is the number of edges where one endpoint is in the trio, and the other is not.
Return the minimum degree of a connected trio in the graph, or -1 if the graph has no connected trios.
Example 1:
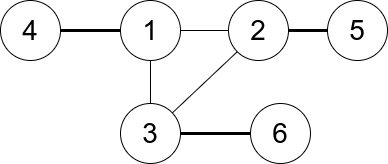
Input: n = 6, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[3,2],[4,1],[5,2],[3,6]] Output: 3 Explanation: There is exactly one trio, which is [1,2,3]. The edges that form its degree are bolded in the figure above.
Example 2:
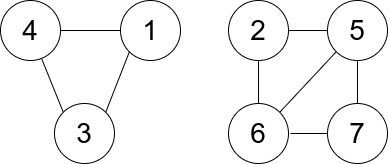
Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,3],[4,1],[4,3],[2,5],[5,6],[6,7],[7,5],[2,6]] Output: 0 Explanation: There are exactly three trios: 1) [1,4,3] with degree 0. 2) [2,5,6] with degree 2. 3) [5,6,7] with degree 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 400edges[i].length == 21 <= edges.length <= n * (n-1) / 21 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi- There are no repeated edges.
Solutions
Solution: Brute Force
- Time complexity: O(n3)
- Space complexity: O(n2)
JavaScript
js
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @return {number}
*/
const minTrioDegree = function (n, edges) {
const indegree = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => 0);
const connected = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => new Array(n + 1).fill(false));
let result = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
for (const [u, v] of edges) {
indegree[u] += 1;
indegree[v] += 1;
connected[u][v] = true;
connected[v][u] = true;
}
for (let u = 1; u <= n - 2; u++) {
for (let v = u + 1; v <= n - 1; v++) {
if (!connected[u][v]) continue;
for (let k = v + 1; k <= n; k++) {
if (!connected[v][k] || !connected[u][k]) continue;
const degree = indegree[u] + indegree[v] + indegree[k] - 6;
result = Math.min(degree, result);
}
}
}
return result === Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ? -1 : result;
};