1353. Maximum Number of Events That Can Be Attended
Description
You are given an array of events where events[i] = [startDayi, endDayi]. Every event i starts at startDayiand ends at endDayi.
You can attend an event i at any day d where startTimei <= d <= endTimei. You can only attend one event at any time d.
Return the maximum number of events you can attend.
Example 1:
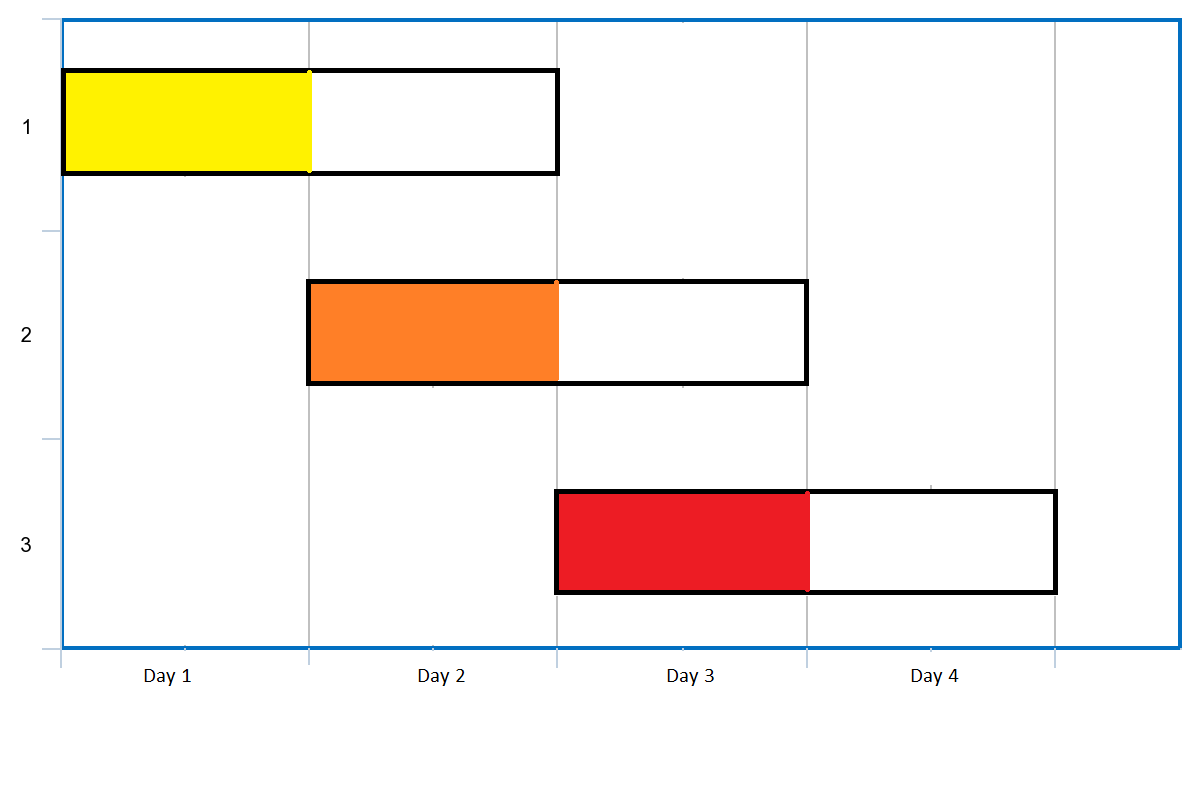
Input: events = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]] Output: 3 Explanation: You can attend all the three events. One way to attend them all is as shown. Attend the first event on day 1. Attend the second event on day 2. Attend the third event on day 3.
Example 2:
Input: events= [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,2]] Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= events.length <= 105events[i].length == 21 <= startDayi <= endDayi <= 105
Solutions
Solution: Priority Queue
- Time complexity: O(nlogn)
- Space complexity: O(n)
JavaScript
js
/**
* @param {number[][]} events
* @return {number}
*/
const maxEvents = function (events) {
const n = events.length;
const endDayHeap = new MinPriorityQueue();
let currentDay = 0;
let index = 0;
let result = 0;
events.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
while (index < n || endDayHeap.size()) {
if (!endDayHeap.size()) {
const startDay = events[index][0];
currentDay = startDay;
}
while (index < n && events[index][0] <= currentDay) {
const endDay = events[index][1];
endDayHeap.enqueue(endDay);
index += 1;
}
result += 1;
currentDay += 1;
endDayHeap.dequeue();
while (endDayHeap.size() && endDayHeap.front() < currentDay) {
endDayHeap.dequeue();
}
}
return result;
};