802. Find Eventual Safe States
Description
There is a directed graph of n nodes with each node labeled from 0 to n - 1. The graph is represented by a 0-indexed 2D integer array graph where graph[i] is an integer array of nodes adjacent to node i, meaning there is an edge from node i to each node in graph[i].
A node is a terminal node if there are no outgoing edges. A node is a safe node if every possible path starting from that node leads to a terminal node (or another safe node).
Return an array containing all the safe nodes of the graph. The answer should be sorted in ascending order.
Example 1:
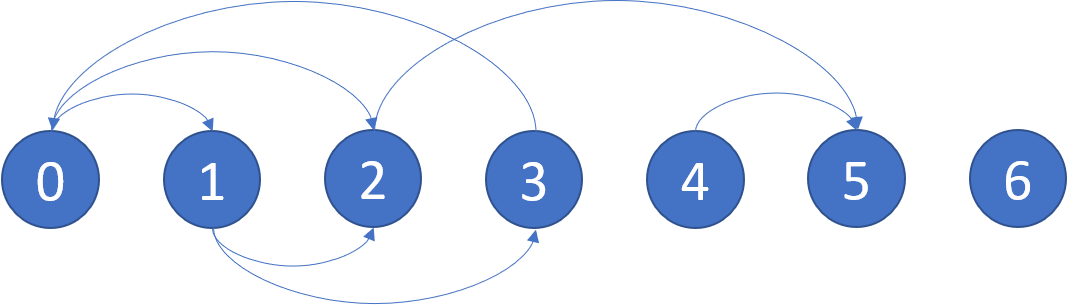
Input: graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]] Output: [2,4,5,6] Explanation: The given graph is shown above. Nodes 5 and 6 are terminal nodes as there are no outgoing edges from either of them. Every path starting at nodes 2, 4, 5, and 6 all lead to either node 5 or 6.
Example 2:
Input: graph = [[1,2,3,4],[1,2],[3,4],[0,4],[]] Output: [4] Explanation: Only node 4 is a terminal node, and every path starting at node 4 leads to node 4.
Constraints:
n == graph.length1 <= n <= 1040 <= graph[i].length <= n0 <= graph[i][j] <= n - 1graph[i]is sorted in a strictly increasing order.- The graph may contain self-loops.
- The number of edges in the graph will be in the range
[1, 4 * 104].
Solutions
Solution: Depth-First Search
- Time complexity: O(n+E)
- Space complexity: O(n)
JavaScript
js
/**
* @param {number[][]} graph
* @return {number[]}
*/
const eventualSafeNodes = function (graph) {
const n = graph.length;
const SAFE = 0;
const CYCLE = 1;
const visited = Array.from({ length: n }, () => false);
const states = Array.from({ length: n }, () => -1);
const result = [];
const isSafeNode = node => {
if (visited[node]) return false;
if (states[node] !== -1) return states[node] === SAFE;
visited[node] = true;
for (const neighbor of graph[node]) {
states[neighbor] = isSafeNode(neighbor) ? SAFE : CYCLE;
if (states[neighbor] === CYCLE) return false;
}
visited[node] = false;
states[node] = SAFE;
return true;
};
for (let node = 0; node < n; node++) {
if (isSafeNode(node)) result.push(node);
}
return result;
};